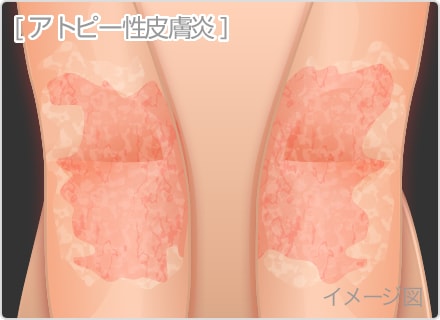
Atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema, is a skin condition that causes the skin to itch on and off.
Some people may have an onset of atopic dermatitis from infancy that eventually goes into remission. Others may continue to experience recurring symptoms into adulthood.
The rate of occurance for atopic dermatitis is approximately 17% in elementary first grade and drops to 10% in junior high school. Oftentimes, the severity of the symptoms decrease as the child grows older.
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis

Reference Images:第一三共ヘルスケア「くすりと健康の情報局」
While there are many possible causes of atopic dermatitis, this type of eczema is often caused by a “allergic predisposition” and hypersensitiity of the organs, including a weak skin barrier function.
Allergic predisposition has two components. One is the presence of the certain allergies in the patient or their family member which may include bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, or atopic dermatitis.
Another is a tendency to produce Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. Often in the case of mild dermatitis, the total IgE level is low.
In most cases, the eczema gets worse with the lack of active treatment. However, one’s work or daily living environment may also play a part in triggering dermatitis. Dust, dust mites, animal hair, other common allergens (substances that cause allergy symptoms), temperature, humidity, alcohol consumption, a common cold, and mental stress could all affect the condition of dermatitis.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by the symmetrical appearance of its symptoms.
It can take form of an itchy rash that persists over a long period of time (more than two months for infants and more than six months for young children).
Symptoms appear on different parts of the body depending on the age of the patient, from infancy and childhood to adolescense and adulthood. Some areas they appear include the forehead, around the eyes and mouth, lips, ears, neck, arm and leg joints, and trunk.
With infants, the rash forms on the head and gradually descends to the extremities. With young children, the rash is seen on the neck and limb joints. After puberty, it is commonly seen on the upper body, including the head, neck, and chest.
Infectious diseases such as molluscum contagiosum (water warts), impetigo contagiosa (impetigo), and Kaposi’s varicella-like rashes may also occur alongside dermatitis.
In severe cases of atopic dermatitis, the itch may be so unbearable, forcing the patient to rub or scratch their eyes, which might lead to eye-related symptoms like cataracts and detached retinas.
Diagnosis of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis can be diagnosed by its appearance, as it is a characteristic skin rash. In addition, it is important to assess the severity of the disease in order to provide appropriate treatment. We will evaluate how much area of the body surface is affected by the rash and how severe the rash is, such as sores or exudates. Blood tests such as serum IgE level, peripheral blood eosinophil count, and serum TARC level will also be performed to help determine the severity of the disease.
Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis used to be a difficult condition to control, but with the emergence of general treatments such as injections and oral medication, it has become possible to control its symptoms to a level that does not interfere with daily life.
Examination and countermeasures for aggravating factors of atopic dermatitis
Saliva, sweat, hair contact, and friction against clothing are factors that exacerbate atopic dermatitis. Care should be taken with hair styles and clothing material. One should also be careful not to leave any soap or shampoo unrinsed. It is also effective to cut fingernails short to minimize irritation when scratching the skin. In addition, it is important to recognize allergens that aggravate dermatitis, such as mites, pollen, animals, fungi, and food, and to take the appropriate countermeasures.
At our clinic, with just a single blood draw sample, we can test for 39 common allergens that could easily trigger allergic reactions. (Covered by insurance)
Topical therapy for atopic dermatitis
The main focus of pharmacotherapy, or therapy of using pharmaceutical drugs for medication, is to control itching and inflammation. Persistent inflammation reduces the skin’s barrier function. Itching causes the scratching of the skin, which in turn worsens the dermatitis. This treatment is most important for reducing these factors. Topical steroids are the basic drug for atopic dermatitis. The steroids’ strength depends on the lesion, and it is a safe drug to use, when taken appropriately.
» Click here for more information on topical steroids.
Protopic (tacrolimus) is mainly used on the face and neck. Unlike steroids, Protopic does not have the side effect of thinning the skin, so it does not cause capillaries to widen and the face to become red. Also, because of its large molecular weight, it can be used for a long period of time without being absorbed, even when applied to normal skin. However, it may take time to get used to it because of the burning sensation it has when applied. This medication may improve the condition of patients who have had poor results with topical steroids. When combined approrpiately with steroids, it can make the treatment more effective.
» Click here for more information on Protopic Ointment.
In addition to topical application, anti-allergic medications can be taken internally to reduce itching.
» Click here for more information on antiallergic medications.
Corectim (delgocitinib), a medication launched in 2020, is a new option for long-term use because it is less likely to cause effects. It is available for children from the age of two, giving atopic dermatitis patients a wider range of options for treatment.
Recent Approaches for Topical Medication
A conventional recommendation for atopic dermatitis is to use reactive treatment. This would be controlling dermatitis solely using moisturizers and treating the inflammation with steroids and other drugs from when it appears until the symptoms subside. More recently, a proactive treatment method has been newly recommended, in which preventive treatment is given before symptoms appear. In the case of atopic dermatitis, which is a frequently recurring condition, the treatment is particularly effective in reducing the amount of anti-inflammatory medication applied without discontinuing the treatment, even long after the inflammation has subsided. This method firmly controls the inflammation. Our clinic also offers any guidance needed regarding this treatment.
Systemic Therapy
There has been an increasing number of systemic treatments for patients with moderate to severe cases of atopic dermatitis. For these patients, conventional treatment has not been effective in controlling their condition. Systemic therapy refers to the treatment of the entire body, as opposed to the treatment of the affected areas topically. The conventional oral immunosuppressant drug, Neoral (cyclosporine), comes with side effects such as high blood pressure and renal dysfunction, making long-term use impossible.
Biologic Medication
Biologics are drugs produced by biotechnological technology, made by applying protein substances that are sythesized by living organisms. They are administered by injection or through intravenus infusion. Dupixent (dupilumab), a drug characterized as a biologic, was launched in 2018. Injected every two weeks in combination with applying topical medications, Dupixent is highly effective against skin rashes and itching. The drug has few side effects and is easy to use for long-term remission.
» Click here for more information on Dupixent
Mitchga (nemolizumab) is a biologic medication launched in 2022 that is effective against itching.
JAK Inhibitors
Janus Kinase inhibitors (or JAK inhibitors) are oral medications that improve atopic dermatitis by inhibiting Janus Kinases, which play an important role in signaling intracellular immune activation and suppressing excessive activation of the immune response. Both Dupixent and Mitchga have been previously used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and have known side effects.
In 2020, Olumiant (baricitinib) was added to the approved list of treatments for atopic dermatitis. It is an oral medication taken once a day that acts as a strong suppressor of JAK1 and JAK2.
In 2021, RINVOQ (upadacitinib) was added to the approved list of treatments for atopic dermatitis. It is an oral medication taken once a day that selectively inhibits JAK1.
At the end of 2021, Cybinqo (abrocitinib) was launched. It is an oral medication taken once a day that selectively inhibits JAK1, and one of its advantages is that its dosage can be increased or decreased.
Although these systematic treatments for atopic dermatitis are very expensive, there are various medical grants available to reduce the financial burden. They are worth considering for patients with atoipc dermatitis who find it difficult to control their condition with conventional treatment.
Some patients would prefer to avoid injections when given the choice of treatment between oral medication and injection. However, there are many other things to consider in addition to the method of administrating treatment. At our clininc, we select the most suitable treatment method using a comprehensive assessment of our patients’ symptoms, their lifestyles, the treatment’s effectiveness and any possible side effects. Please contact us if you are interested.
Skin Care
Skin care is very important in order to restore any barrier function and moisture retention of the skin. Although pharmacotherapy is important, routine skin care plays a very important role in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Keeping the skin clean (taking a bath, showering, etc.) prevents skin symptoms from worsening, and using moisturizers and protectants retores the skin’s barrier function and prevents allergens from entering the skin.
For people who have atopic dermatitis, the skin is dry even if it may not appear so. Therefore, it is necessary to apply moisturizer to the entire body. In addition, to reduce the risk of developing atopic dermatitis in infants, topical moisturizers should be applied immediately after birth.
To prevent dryness, you must take baths at temperatures between 38℃ and 40℃ and wash the body with soap. If the skin is severely dry or experiencing a period of intense dryness, it is recommended to use soap less frequently or to use soap products that contain less additives and hypoallergenic properties.
Prevention and precautions for atopic dermatitis
The first preventive measure is to keep the skin moist and clean by bathing and such. Scratching damages the skin and worsens its condition, so it is important to avoid scratching and itching the skin.
Atopic dermatitis is a condition that is difficult to cure completely. It is not easy to suddenly stop the medication when reducing the dosage, and even if there are no apparent symptoms, continued use of topical medication is necessary if the condition reoccurs repeatedly. It is important to deal with atoipc dermatitis by patiently applying topical medication and paying attention to your daily lifestyle.
What we do for children
Many patients with atopic dermatitis are children and may not be able to care for themselves well at home. At our clinic, we try to actively involve the child in treatment with the following efforts.
Involving Children in Treatment
It is important to continue to apply the medication in order to control atopic dermatitis. However, young children may not like sticky or cold ointments, or they may not be able to sit still and apply them. This can be resolved by motivating them to do so. When the child realizes that they can apply the medication by themselves, they will often become very good at it.
At our clinic, we believe in the importance of motivating our patients to apply their medication, so we discuss and decide on the choice of medication with them. We allow the children to try out their preferred method of treatment (ointment, cream, lotion, spray, or foam). For example, to children who did not want to apply medication to their faces, trying a type of medication with a silky base allowed them to feel like it was something they were able to control and apply on themselves.
Reducing the time and effort required for skin care.
The basis of atopic dermatitis treatment is to moisturize the skin and reduce inflammation. Although separate medications must each be applied as treatment, some patients do not continue their skin care because of the time and effort it takes to apply two different medicines. We offer our two-in-one treatment which mixes moisturizer and anti-inflammatory medication together, so only one application is needed for the skin care routine. With these efforts, we are proposing a treatment that can continue to be used for a long time.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How do you treat mild atopic dermatitis?
-
Keep the skin well moisturized and apply steroids or other such topical agents to the inflamed areas.
- Are there any herbal remedies that are effective with atopic dermatitis?
-
At our clinic, we often prescribe a medicine called Hochuekitto.