What is psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a condition which includes the reddening of the skin and the formation of crusty and flakey white scabs that resemble dandruff on top of raised patches of the skin. The white scabs, also called scales, are made up of dead keratinized skin cells. When those scales are forcibly peeled off, it results in a petechial hemorrhage called the Auspitz phenomenon. The normal turnover period for the skin is about 45 days, but with psoriasis, the turnover period is 4 to 7 days. This is about 10 times faster than the rate of metabolism, with the skin multiplying abonormally.
Psoriasis can occur anywhere on the skin, but it is more common on the hairline, scalp, knees, elbows, and any other area that is frequently exposed to external stimuli. Many people suffer from itching, and scratching worsens the condition. Psoriasis is common among middle-aged men and affect about 1 in every 300 people in Japan. Patients with psoriasis are 65% male.
There are several types of psoriasis. The majorite of patients have plaque psoriasis vulgaris, a condition in which white, keratinized plaque covers the red patches of the skin. It is estimated that 20% of people with psoriasis also suffer from nail peeling, deforminities, and other abnormalities, including arthritis.
People Who Think They May Have Psoriasis
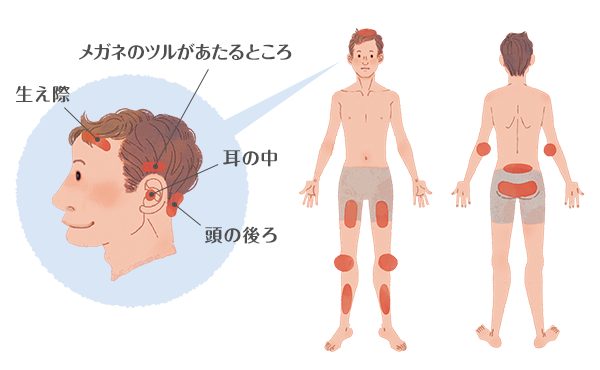
It’s possible that you may have psoriasis if distinct red spots appear on your body. Symptoms for psoriasis are commonly spotted on the scalp, the outer elbows, the kneecaps (knee pads), and the hips.
Symptoms resemble rashes and tinea corporis, also known as ringworm of the body, which is caused by infection of the body with athlete’s foot fungus (trichophyton rubrum). While it is difficult to differentiate these conditions from psoriasis, dermatologists can usually tell the difference. A skin examination is performed to make a more definitive diagnosis with ringworm. In rare cases, when psoriasis is difficult to diagnose, a biopsy may be performed under local anesthesia to remove a portion of the skin.
The molecular weight of the active ingredients is large, so it is believed that
Initial Symptoms of Psoriasis
Redness and itching are the initial symptoms of psoriasis in most patients. These initial symptoms are so similar to eczema that a normal person would not be able to tell that it is psoriasis just by looking at or touching it. Also, in the case of a physician’s diagnosis, a skin biopsy, in addition to a medical interview and visual examination, will help to identify the disease.
In the case of psoriasis, as the symptoms progress, the borders of the disease become more distinct and raised and scaly. Eczema can cause dermatitis, rashes, blisters, sores, and even infection of the affected area, which may cause that area to become sore.
Psoriasis of the pubic area
Psoriasis can also appear on the pubic area because the skin symptoms are caused by external stimuli. However, the frequency of occurrence is not so high. Because the pubic area is moist, it can cause rashes and tinea infections. If symptoms occur only on the pubic area, some condition other than psoriasis may be suspected, so please consult us.
Causes of Psoriasis
The cause of psoriasis is not known, but it is believed to be related to a variety of factors. It is said one cause may be related to one’s predisposition of psoriasis – whether or not there has been history of psoriasis in the family or physical stimuli such as injuries, infections, medications, and stress. Another possible cause is an immune disorder in which the immune system, which is supposed to protect the body, is said to run out of control, causing skin abnormalities.
The symptoms of psoriasis may get better or worse, but the overall condition persists. Scratching and rubbing the area can trigger the symptoms to worsen, and dryness is also a major enemy. Lifestyle factors such as binge eating, lack of sleep, and stress can also worsen psoriasis.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is characterized by the Auspitz phenomenon, in which thickened plaques bleed in spots when forcibly peeled off. In addition, rubbing the skin without lesions or injuring the skin can cause Kevnel’s phenomenon, in which new lesions appear, which can aggravate the condition. Psoriasis can be diagnosed by the progression of symptoms, such as characteristic skin lesions, the Auspitz phenomenon, and the Kevnel phenomenon.
When considering the possibility of other diseases, a histopathological examination of the lesions under a microscope and some blood sampling tests are included.
If psoriatic arthritis is present, it is difficult to distinguish it from rheumatoid arthritis, so joint x-rays and ultrasound examinations are also performed.
Psoriasis Treatments
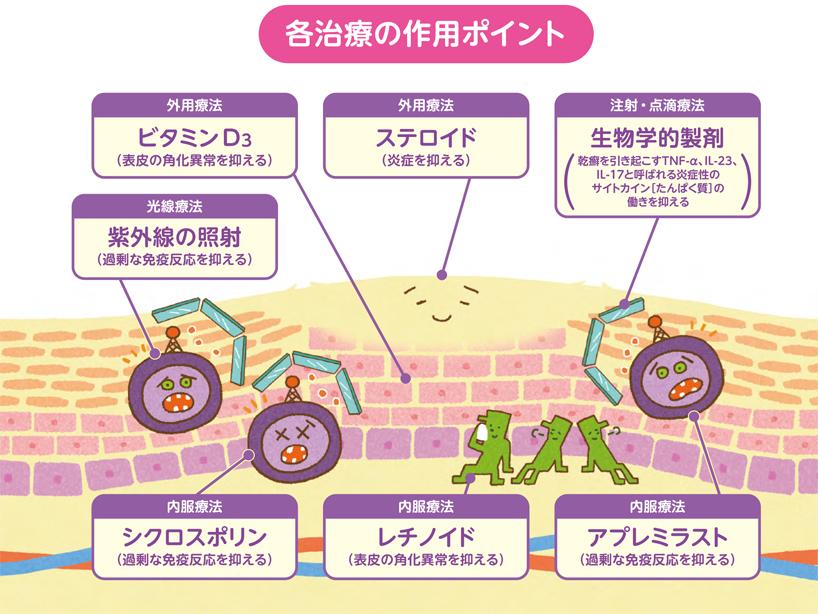
There are four major treatments for psoriasis (ointments, oral medications, injections, and phototherapy). The basic treatment is topical application of the active vitamin D3 products (Oxarol, Dovonex, Bonalfa-high, etc.) and steroids. Steroids suppress inflammation, while vitamin D3 helps to regulate skin metabolism and normalize the skin. Recently, a combination of vitamin D3 and steroids (Marduox, Dovobet) has been widely used. These drugs are easy to use because there is no need to apply them in layers and they only need to be applied once a day.
For psoriasis of the scalp, a product called Comclo shampoo containing a strong steroidal ingredient has also been on the market since July 2017. It is a shampoo-type topical product that is applied to the scalp and rinsed off in 15 minutes, making it easy to use and reportedly less likely to cause side effects.
When topical treatment is difficult, treatment of psoriasis with retinoids (Tigason), PDE4 inhibitors (Otezla), immunosuppressants (Neoral), and other oral medications is also available.
| Type | Treatment | Effect | Exemplary Drugs and Devices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ointment | Vitamin D3 | suppresses epidermal dyskeratosis |
Oxarol |
| Steroids | suppresses inflammation |
topical steroids | Fixed-dose combination |
Vitamin D3 + Steroids |
Dovobet・ Marduox |
| internal medicine | Retinoids | suppresses epidermal dyskeratosis |
Tigason |
| Immunosuppressants | suppresses excessive activation of the immune response |
Neoral (cyclosporine) |
|
| PDE4 inhibitors | suppresses excessive activation of the immune response |
Otezla (apremilast) |
|
| TYK2 inhibitors |
suppresses excessive activation of the immune response |
Sotyktu (deucravacitinib) |
|
| Phototherapy | UV radiation | suppresses excessive activation of the immune response |
Narrowband UVB and Excimer laser |
| Injection | Biologics | suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokine (protein) movement |
IL-17 Cosentyx (secukinumab) IL-23 Tremfya (guselkumab) Skyrizi (risankizumab-rzaa) TNF-α Humira |
Anti-itch medications are also used alongside the treatment as psoriasis can be very itchy when the lesions appear, and scratching it causes the lesions to spread.
Phototherapy with ultraviolet light is another option if there is no improvement with ointments or oral medications or if the lesions have spread. For many, symptoms improve in the summer, and UV light has been shown to improve psoriasis.
Injections of biologic medication (Cosentyx, Tremfya, Skyrizi, etc.) are used as a more advanced treatment. Biologic treatments are approved for use by the Board of Directors after reviewed by the Biologics Review Committee of the Japanese Dermatological Association.
*Our clinic is included in the Japanese Dermatological Association’s list of “”Facilities Approved for Use of Biologics for Psoriasis””.
»Facilities Approved for Use of Biologics for Psoriasis
Biologics for Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases are caused when the immune system, which originally prevents the invasion of foreign substances such as bacteria and viruses, mistakenly recognizes something in the body as a foreign substance and attacks it.
Psoriasis is caused by the body’s autoimmune response and the cytokines that are produced in the process. Cytokines are proteins that transmit information from cell to cell, and they play and active role during the body’s immune response. Therefore, cytokines are necessary to maintain a healthy body. However, if they are produced in excess for any reason, they can cause inflammation. Cytokines that cause inflammation are called pro-inflammatory cytokines.
With psoriasis, abnormalities in the body’s immune system result in excessive production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Major cytokines include TNF-α, IL-23, and IL-17.
This section describes the immune response occurring in psoriasis. The skin where psoriasis symptoms occur has a large number of dendritic cells that play a part in the immune response. While there are several types of dendritic cells, the ones that are most closely linked to psoriasis are TIP-DCs. TIP-DCs produce a cytokine called TNF-α, which triggers inflammation. TIP-DCs also produce a cytokine called IL-23 (Interleukin-23). IL-23 causes helper T-cells, which are immune cells, to change into Th17 cells. These cells then produce the inflammatory cytokines IL-17 and IL-22. At the same time as causing inflammation and the multiplication of skin cells, IL-17 and IL-22 also cause immune cells to produce TNF-α, further aggravating the inflammation. The increase in TNF-α causes TIP-DCs to become even more active, leading to an increase in Th17 cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines, and the vicious cycle repeats itself. This is how the symptoms of psoriasis progress.
Since 2010, a series of biologics targeting pro-inflammatory cytokines have been developed for the treatment of psoriasis.
List of Biologics for Psoriasis [2023 Edition]
| Brand Name | Generic Name | Classification | Self-injection | PMDA Approved |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REMICADE | infliximab | TNF-α inhibitor |
× | Jan. 2010 |
| HUMIRA | adalimumab | TNF-α inhibitor |
〇 | Jan 2010 |
| CIMZIA | certolizumab pegol |
TNF-α inhibitor |
〇 | December 2019 |
| STELARA | ustekinumab | IL12/23 inhibitor |
× | January 2011 |
| TREMFYA | guselkumab | IL23 inhibitor |
× | March 2018 |
| SKYRIZI | risankizumab‐rzaa | IL23 inhibitor |
× | March 2019 |
| ILUMYA | tildrakizumab-asmn | IL23 inhibitor |
〇 | June 2020 |
| COSENTYX | secukinumab | IL17 inhibitor |
〇 | December 2014 |
| LUMICEF | brodalumab | IL17 inhibitor |
〇 | June 2016 |
| Taltz | ixekizumab | IL17 inhibitor | 〇 | July 2016 |
| Bimzelx | bimekizumab | IL17 inhibitor | × | January 2022 |
Other Psoriasis
Psoriasis vulgaris is the main type of psoriasis, accounting for about 90% of all psoriasis cases, but there are some types that require early treatment.
Generalized Pustular Psoriasis
It is characterized by multiple red blisters filled with pus on the skin of the entire body, often accompanied by a fever. It is a serious illness and requires hospitalization. We will refer you to our affiliate, a university hospital specializing in psoriasis.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic Arthritis is arthritis associated with psoriasis. It can occur even when skin symptoms are mild. It is irreversible and often requires systemic treatment. We will refer you to a university hospital specializing in psoriasis for evaluation of arthritis.
Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate Psoriasis is a skin disease in which small skin rashes shaped like water droplets, about 1 cm in diameter, appear all over the body. It is often caused by a streptococcal infection, and commonly follows tonsillitis or other bacterial infections of the nose, throat, or oral cavity. In many cases, the onset of the disease is sudden and is mainly seen in children and young people. Early treatment is important, since guttate psoriasis may develop into psoriasis vulgaris. Oftentimes, it can be cured by treatment of the streptococcal infection.
Precautions Regarding Psoriasis
Precautions in Daily Life
To reduce irritation to the skin, it is recommended to choose loose-fitting clothes with a comfortable design and cotton fabrics that do not irritate the skin.
It is also important to keep the skin clean. When taking a shower or bath, be careful not to scrub too hard. Be sure to shower or bathe with lukewarm water as hot showers and long baths can increase itching. After getting out of the bath or shower, be sure to moisturize the skin and apply moisturizing cream as soon as possible. During the drier winter months, it is better to use a humidifier to prevent your skin condition from getting worse.
Taking a walk in the sun is also recommended. Ultraviolet rays have the effect of suppressing the immune system, which leads to improvement of symptoms. You may also want to dress in short sleeves, shorts, or any clothing that exposes your skin when taking a walk.
Important Points Regarding Psoriasis (It is not contagious)
Psoriasis is not a contagious disease. It cannot be passed to or received from others. Infection can trigger psoriasis, but psoriasis is an inflammatory condition of the skin, not an infectious disease. In many cases, the symptoms are visible on the skin, leading to discrimination and bullying. It is important for all people, both the patients and the people around them, to have a proper understanding of this disease.